Diabetic Neuropathy is a severe condition arising from diabetes. The high blood sugar in diabetes patients leads to severe nerve damage, especially in the legs, feet, toes, arms, and hands. Typical symptoms of this condition include digestive problems plus pain and numbness in the limbs. But in other patients, Diabetic Neuropathy can be disabling, and painful, and advanced non-invasive spine surgery is recommended.
There are four primary types of Diabetic Neuropathy, and it is vital to note that you can be diagnosed with one or more types. In a nutshell, your symptoms will largely depend on the type you have and the nerves affected.
1. Peripheral Neuropathy
This is the most widespread type, and it affects the lower limbs first (legs and feet), followed by the arms and hands. These symptoms are considerably conspicuous at night, and they include:
- A tingling or burning feeling in the limbs
- Loss of reflexes, notably in the ankles
- Extreme lack of coordination and balance
- Weakness in the muscles
- Numbness that results in reduced ability to sense pain or heat changes
- Heightened sensitivity to touch (The weight of a bedsheet might be too much for some people)
2. Radiculoplexus Neuropathy

This condition is also known as diabetic Amyotrophy, proximal neuropathy, or femoral neuropathy.
Radiculoplexus neuropathy is most commonly found in older adults or Type 2 diabetes patients. It mainly affects the buttocks, hips, legs, and thighs.
The following are the symptoms of this form of Diabetic Neuropathy, and while some symptoms might only affect one side of the body, it can spread to the other side.
- Severe hips, thighs, or buttock pain
- Swelling in the abdomen
- Significant weight loss
- Shrinking and weakness in the thigh muscles
3. Autonomic neuropathy
Do you know that the autonomic nervous system controls the bladder, heart, eyes, stomach, sex organs, and intestines? When Diabetes affects these body parts, the resulting symptoms include:
- Fluctuation in sweat production
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Hypoglycemia unawareness
- Eyes poorly adjusting to the light
- Decreased libido
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Bladder problems (urinary retention, urinary tract infections or urine incontinence)
4. Mononeuropathy
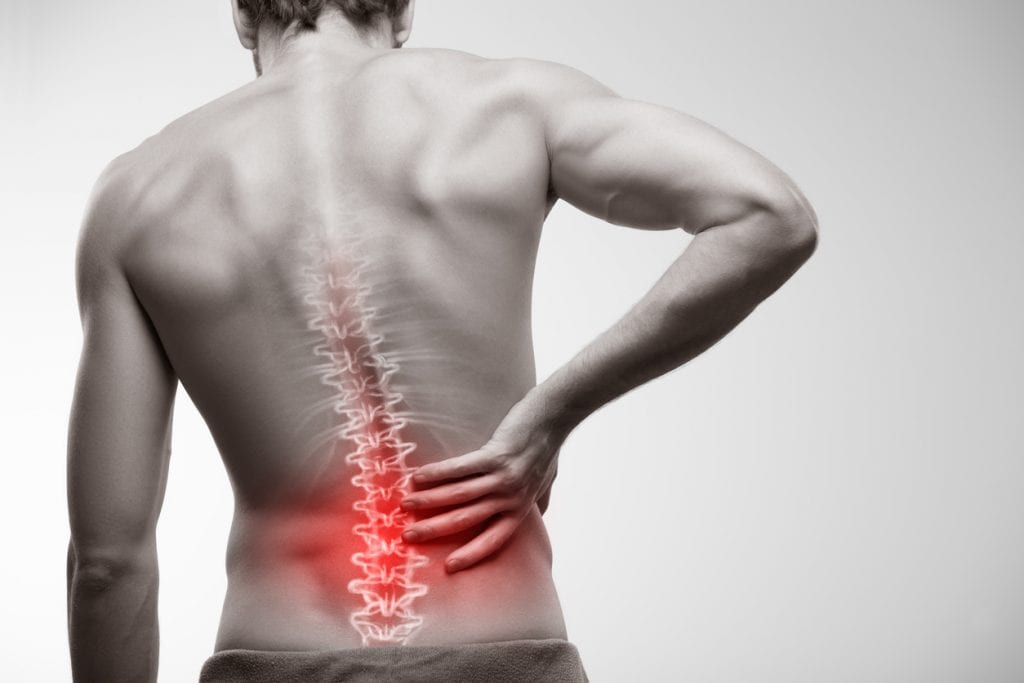
Also known as focal neuropathy, this is damage to a particular nerve situated in the torso, legs, or face. The symptoms largely depend on which nerve has been affected in the following parts of the body:
- Feet or shins
- Abdomen or chest
- Pelvis or lower back
- The front of the thighs
Mononeuropathy is also associated with nerve issues in the face and eyes leading to:
- Double vision
- Pain behind the eyes
- Bell’s palsy
- Difficulty in maintaining focus
If the pain persists, non-invasive spine surgery such as a spinal cord stimulator might be the patient’s best bet of relieving pain.


